Semester 3 - Computer Networks - Prerequisites of Subnetting
Prerequisites for SubnettingPermalink
Let’s have a clear understanding of basic terms before starting actual subnetting.
If you have a foundational knowledge of networking, then you might want to visit the subnetting Ip4
Some important & frequently used termsPermalink
- Bits: The basic unit of digital information, represented as 0 or 1.
- Byte: A unit of digital information that consists of 8 bits.
- IP Address: A unique identifier for a device on a network. Example:
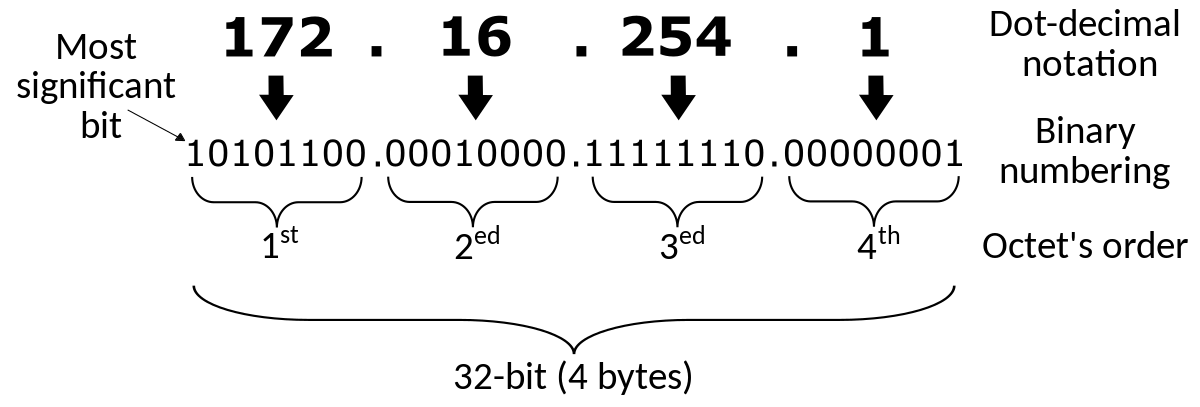
192.168.0.1. - IPv4: An IP addressing system using 32 bits divided in 4 octets.
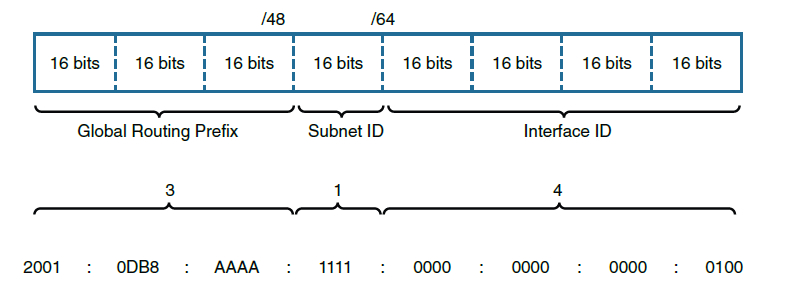
- IPv6: An IP addressing system using 128 bits divided into 8 blocks, 4 hexa digits in each block, each hexa digit represents 4 bits, hence each block is 16 bits.
- Network Address: The identifier for a network, shared by all devices on that network. Example:
192.168.1.0/24where192.168.1.0is the network address. - Host Address: The unique identifier for a device within a network. Example: In
192.168.1.105/24,105is the host address. - Subnet: A division of a network, allowing for smaller, more manageable networks. Example:
192.168.1.0/26and192.168.1.64/26are two subnets of192.168.1.0/24. - Subnet Mask: A mask used to determine what subnet an IP address belongs to.
- Prefix Length: In an IP address notation, the number after the slash indicating the number of bits used for the network prefix. Example: In
192.168.1.0/24,/24is the prefix length meaning first 24 bits out of 32 are used for network. - Network Interface: A device’s hardware or software that connects it to a network. Example: Ethernet or Wi-Fi adapter in a computer.
- Default Gateway: The device that routes traffic from a local network to other networks or the internet. Example: A home router with IP address
192.168.1.1acting as the default gateway for all devices on the network. - Broadcast: A special type of IP address used to send data to all devices in a specific network. Example: The broadcast address for the network
192.168.1.0/24is192.168.1.255. - CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing): An IP addressing scheme that replaces the old system based on classes. It uses a syntax of IP address/Prefix Length, e.g.,
192.0.2.0/24.



