Semester 3 - DSA - Sample Test
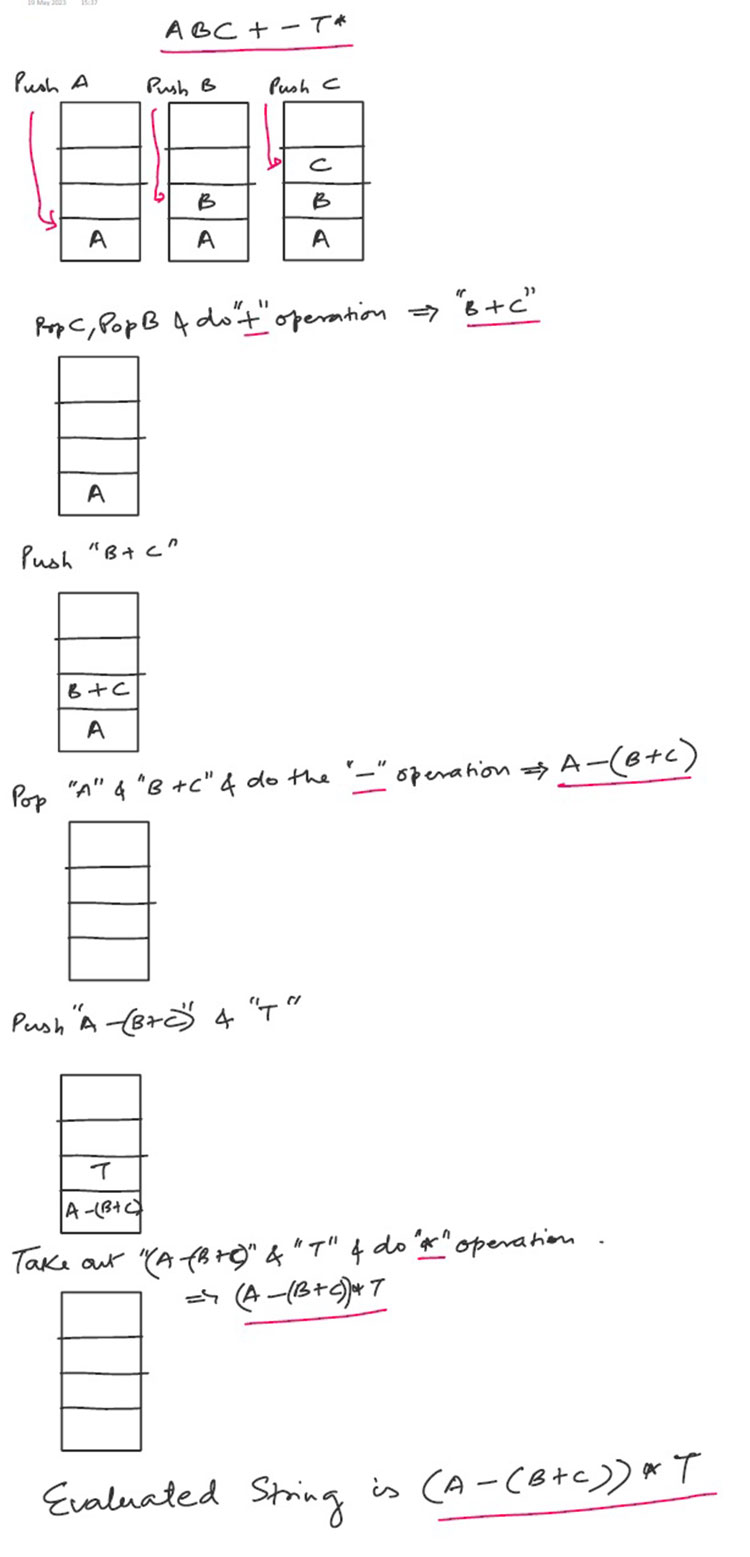
Q1. The postfix form a given string S = ABC+-T, then the find out the S.
A) (A-(B+C))T
B) A+B-CT
C) AB-C+T
D) A*B+C-T
Answer: A) (A-(B+C))*T
Explanation:
Q2. H is a graph with k vertices. H is connected and has exactly k-1 edges, then:
A) H is a tree
B) H contains no cycles
C) Every pair of vertices in G is connected by exactly one path
D) All of these
Answer: D) All of these
Explanation: Formula to calculate no. of edges ‘E’ if number of Nodes/vertices is ‘K’ is E = K-1
Q3. Initially a queue with configuration is p, q, r, s. ‘p’ is at the front. To get the configuration s, r, q, p find the number of deletions and additions are? required
A) 4 deletions, 4 additions
B) 3 deletions, 3 additions
C) 5 deletions, 5 additions
D) 2 deletions, 2 additions
Answer: A) 3 deletions, 3 additions
Explanation: remove p,q,r and insert r, q, p in order.
Q4. The traversal technique which lists the nodes of a binary search tree in ascending order?
A) post-order
B) in-order
C) pre-order
D) linear order
Answer: B) in-order
Explanation:
- In-order (Left, Root, Right) —> Ascending order (left is smaller than root, right is greater than root)
- Pre-order (Root, Left, Right)
- Post-order (Left, Right, Root)
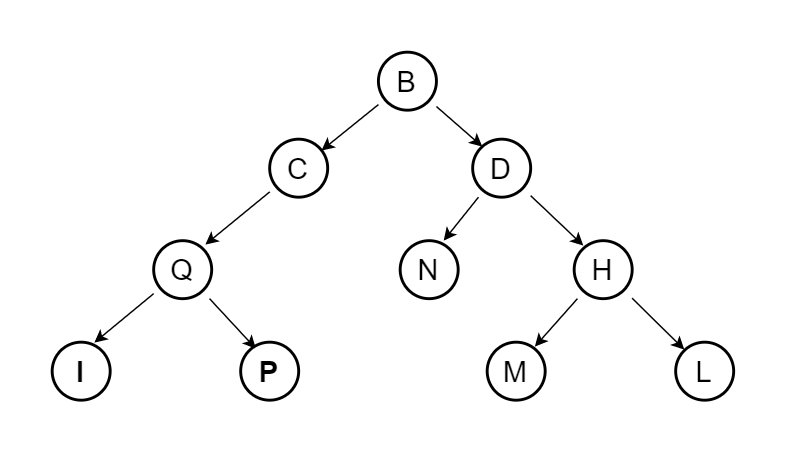
Q5. Given a binary tree whose in order and preorder traversal are given below:
Preorder: BCQIPDNHML
In order: QICPBNDMHL
The post order traversal of the above binary tree is:
A) QICPNHDMLB
B) QICPHNDMLB
C) QICPNHDMBL
D) IPQCNMLHDB
Answer: D) IPQCNMLHDB
Explanation: See Question 2 Here
In our case, B is root, and graph would be
Q6. The postfix expression AB+CD–* can be evaluated using a
A) Stack
B) Tree
C) Queue
D) Linked list
Answer: A) Stack
Explanation:
- Push ‘A’, ‘B’ into stack
- Pop ‘A’, ‘B’ and perform ‘+’ operation
- Push ‘A+B’ into stack, Push ‘c’ & ‘D’ into stack
- Pop ‘C’ & ‘D’ and perform ‘-‘ operation
- Push ‘C-D’ into stack
- pop ‘A+B’ and ‘C-D’ from stack and perform ‘*’
- push ‘(A+B)*(C-D)’ into the stack
Q7. A binary search tree is a binary tree:
A) All items in the left sub-tree are less than root
B) All items in the right sub-tree are greater than or equal to the root
C) Each sub-tree is itself a binary search tree
D) All of the above
Answer: D) All of the above
Explanation: order is left side < root < right side
Q8. The In-order traversal of the tree will yield a sorted listing of elements of tree in
A) Binary tree
B) Binary search tree
C) Heaps
D) None of the above
Answer: B) Binary search tree
Explanation: In a binary search tree, the left subtree of a node contains values smaller than the node, and the right subtree contains values greater than the node
Q9. How many binary trees formed with 5 nodes is
A) 22
B) 46
C) 120
D) 42
Answer: D) 42
Explanation: Formula is 2n!/(n+1)!n!
The number of binary trees for 1 to 10 nodes should be 1, 2, 5, 14, 42, 132, 429, 1430, 4862, 16796
Q10. The following postfix expression is evaluated using a stack 823^/52* + 41* – The top two elements of the stack after first * is evaluated
A) 8, 10
B) 4, 25
C) 2, 25
D) 1, 10
Answer: D) 1, 10
Explanation:
Step 1: Push 8, 2, and 3 onto the stack.
Stack: [8, 2, 3]
Step 2: Pop 3 and 2 from the stack, evaluate 2^3 = 8, and push the result (8) onto the stack.
Stack: [8, 8]
Step 3: Pop 8 and 8 from the stack, evaluate 8 / 8 = 1, and push the result (1) onto the stack.
Stack: [1]
Step 4: Encounter ‘5’, push it onto the stack.
Stack: [1, 5]
Step 5: Encounter ‘2’, push it onto the stack.
Stack: [1, 5, 2]
Step 6: Pop 2 and 5 from the stack, evaluate 5 * 2 = 10, and push the result (10) onto the stack.
Stack: [1, 10]
Q11. The operations where the worst case time complexity of AVL tree is better while comparing with binary search tree for
A) Search, Delete and Insert Operations
B) Search and Delete Operations
C) Insert and Delete Operations
D) Search, and Insert Operations
Answer: A) Search, Delete and Insert Operations
Q12. Suppose an empty stack performing operations in the given order: push(1), push(2), Pop, push(3), push(4), push(5), Pop, what is the top of the stack?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
Answer: D) 4
Q13. What is the minimum number of nodes in a binary tree of depth k (root is at level 0).
A) 2 k – 1
B) 2 k+1 – 1
C) k + 1
D) k
Answer: C) k + 1
Explanation: Assuming one node at each level, minimum number of nodes with depth/level k is K+1
And the maximum number of nodes with depth/level k is 1 + 2 + 4 + …+ 2k = 2k+1 - 1
Q14. Which is the efficient data structure to insert or delete a number in a stored set of numbers is
A) Binary tree
B) Linked list
C) Doubly linked list
D) Queue
Answer: C) Doubly linked list
Q15. Suppose a queue is implemented with a linked list, and keeping track of a front pointer and a rear pointer, during an insertion into a non-empty queue which these pointers are changed?
A) Only rear pointer changes
B) Only front pointer changes
C) Neither of the pointers change
D) Both of the pointers changes
Answer: A) Only rear pointer changes
Q16. In linked list implementation of a queue, front and rear pointers are tracked. Which of these pointers will change during an insertion into an EMPTY queue?
a) Only front pointer
b) Only rear pointer
c) Both front and rear pointers
d) No pointer will be changed
Answer: c) Both front and rear pointers
Q17. What is the maximum number of parentheses that will appear on the stack at any one time for a parenthesis expression given by ( () (()) (()) ) ))
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5
Answer: B) 3
Explanation:
- Push “(“ onto the stack: [ ( ]
- Push “(“ onto the stack: [ (, ( ]
- Match “)” with the top of the stack: [ ( ]
- Push “(“ onto the stack: [ (, ( ]
- Push “(“ onto the stack: [ (, (, ( ]
- Match “)” with the top of the stack: [ (, ( ]
- Match “)” with the top of the stack: [ ( ]
- Match “)” with the top of the stack: [ ]
At any point during the evaluation, the maximum number of parentheses on the stack is 3.



